ABS developed its
Guidance Notes on Safety Culture and Leading Indicators of Safety (2012) with the objective of improving safety performance in the management and operation of cargo-carrying commercial vessels. ABS provides this guidance in recognition of the beneficial effect that a positive safety culture can have on safety performance, and the part played by leading indicators in guiding action to improve safety performance. The ABS Guidance Notes provide:
- Guidance to maritime organizations on the survey and assessment of their organizational safety culture, both onshore and at sea
- A process for identifying an organization's leading indicators of safety performance
Leading indicators are safety metrics that are associated with, and precede, an undesirable/unexpected consequence such as an operational incident, near miss or personal injury. Tracking and improving these safety metrics may help to maintain and improve safety performance. The results from the survey, and/or any leading indicators, can be incorporated into the organization's ongoing corporate social responsibility (CSR) and continual improvement program. Additionally, they can:
- Reveal areas of weakness in advance of adverse events
- Be associated with proactive activities that identify hazards
- Aid risk assessment and management
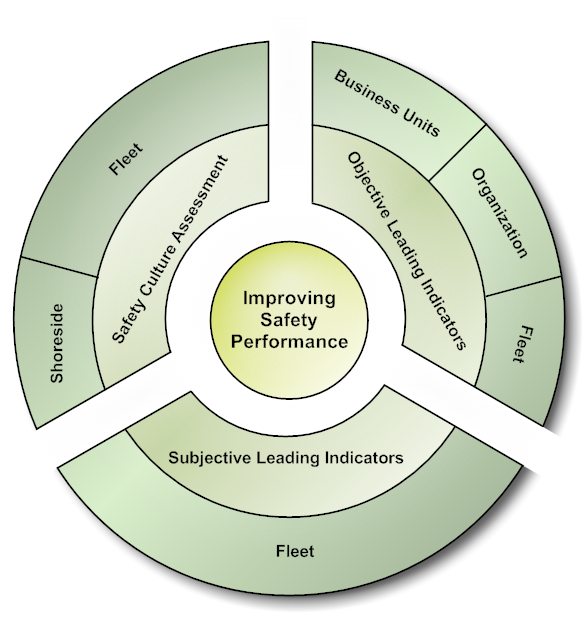
Some examples of leading indicators of safety include the size of the safety budget, the safety audit scores, the number of safety inspections and the number of safety meetings involving management. Leading Indicators are the most important safety culture metrics for the organizations as they correlate with the organization's safety performance. The ABS Safety Culture and Leading Indicators Model demonstrates the approach ABS has taken to assess safety performance.
The ABS Safety Culture and Leading Indicators Model